Maximizing safety and performance with integral leak testing
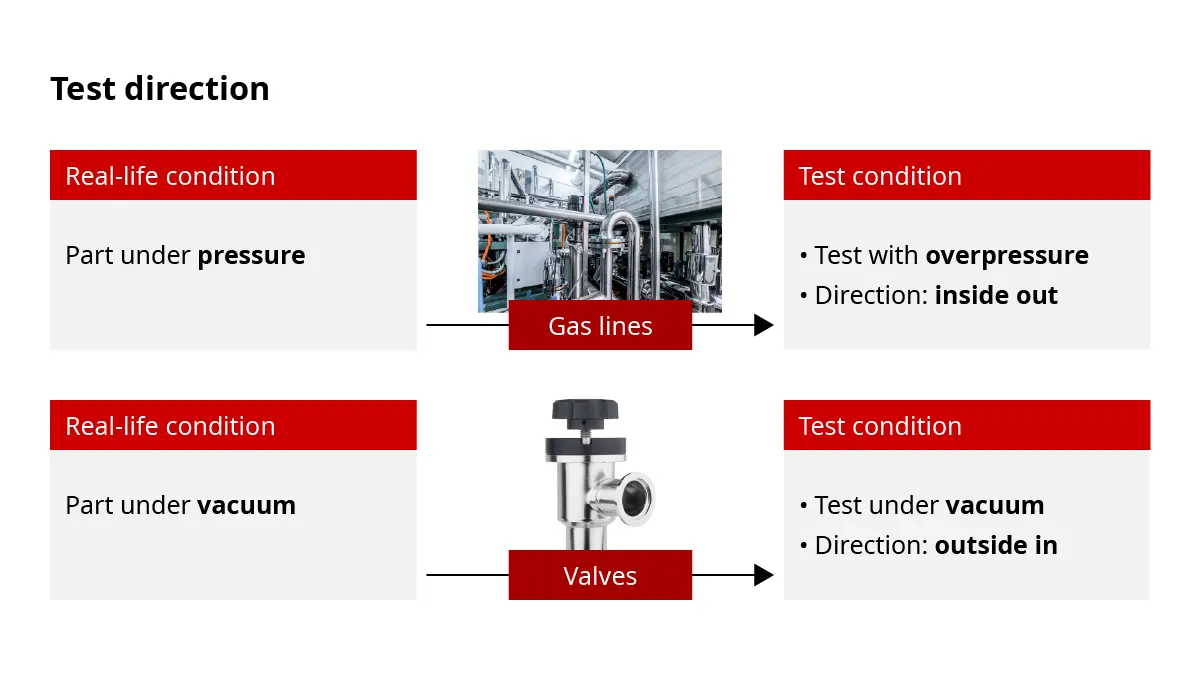
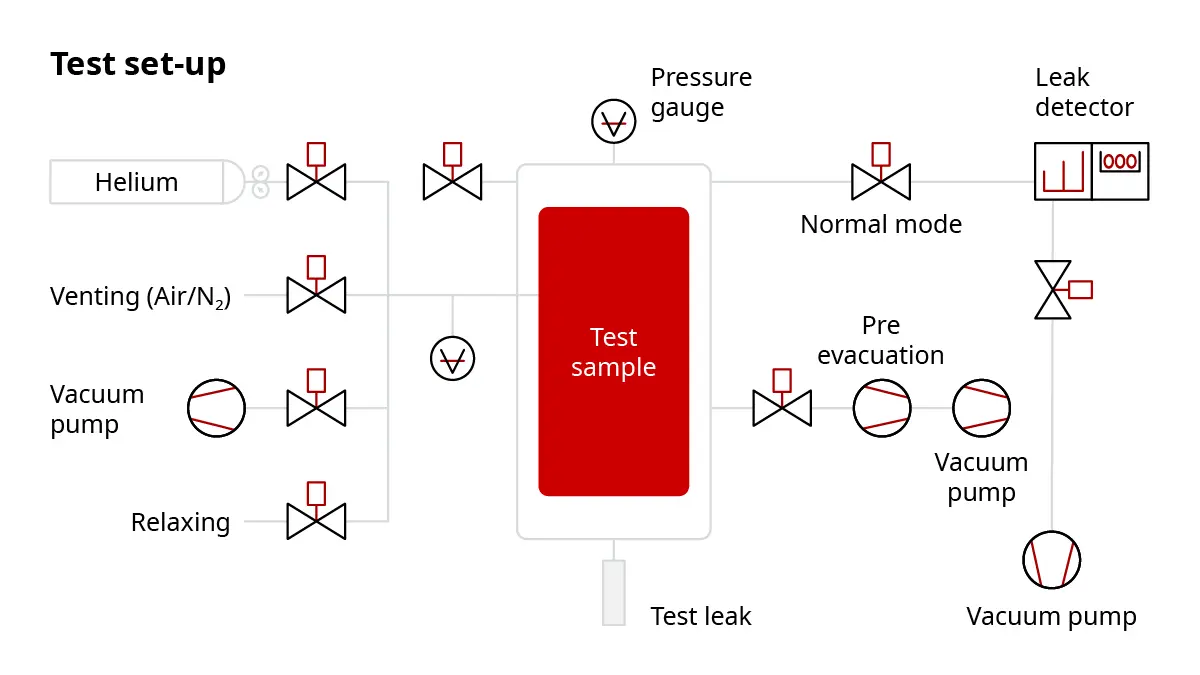
Integral leak testing (accumulation or hard vacuum test) is not only about meeting standards – it is essential for ensuring product safety, quality and functionality by measuring the total leak rate of a test specimen or vessel under vacuum or positive pressure conditions.While several leak detection methods exist, each suited to different technical and functional requirements, integral leak testing has emerged as one of the most widely used approaches in industrial applications.
Learn how to select the right leak detection method and understand how pressure differences impact results in our FAQ section.
By detecting unacceptable leak rates, integral leak testing ensures:
- Product reliability: It guarantees that products function reliably across their lifecycle, mitigating potential failures.
- Environmental compliance: The testing minimizes ecological impacts, aligning with environmental standards.
- Industry conformity: It plays a crucial role in optimizing production and maintaining strict adherence to industry standards.