Quadrupole Mass Spectrometers
Devices for analyzing gas compositions

Mass spectrometry is a widely used analytical method for looking at the chemical composition of substances. Our devices for (residual) gas analysis all feature a quadrupole mass spectrometer (QMS) at their core.
Basic components
Detectors
Depending on the operating pressure, different detectors are used: The Faraday detector (F) works at higher pressures compared to the combined Faraday/C-SEM detector (M), which requires a lower pressure. This difference, however, affects the detection limits. The exact values also depend on the residence time and the ion source used.
Configurable RGA systems
Every test task is unique. Besides our standard OmniStar and ThermoStar solutions, our experts use the full range of Pfeiffer products to configure a system tailored to your needs. One example is our OmniGrade RGA cleanliness verification system.
Hardware connection
The following hardware connections are available for integrating our devices:
- PrismaPro: DN 40 CF flange
- HiQuad Neo: DN 63 CF flange
- OmniStar and ThermoStar: Capillary hose or suitable adapter (1/4" / DN 16 ISO-KF)
Software and interfaces (Ethernet)
PV Mass Spec software is easy to use and provided with your device purchase. Updates are available online. Our mass spectrometers also offer various interfaces to communicate directly with a PLC.
Suitable mass spectrometers for various applications

Before selecting the equipment, clearly define the analysis task and the goal you aim to achieve. Consider the following criteria:
Measuring speed
The measuring speed can be adjusted depending on the analysis task. For example, with the PrismaPro, it ranges from a minimum of 1 ms up to 16 s. The measuring speed influences the amount of noise in both the signal and the background.
Resolution
The resolution can be adjusted based on the application area, mainly through the software. It affects separation and signal height. A standard resolution is commonly used.
Masses to be detected
Determine which masses are required for your application. Opt for the smallest suitable mass range to ensure better sensitivity (signal).
Detection limit
The detection limit is influenced by the sensitivity and peak overlap. Sensitivity also varies depending on the detector used (Faraday vs. Faraday/SEM).
FAQ
What types of mass spectrometers are there?
The main difference between various mass spectrometers lies in the separation system. The types are categorized accordingly:
- Sector field devices use the deflection effect of a magnetic field on moving charge carriers.
- Time of flight mass spectrometers (TOF) utilize the different speeds of particles with the same energy for separation.
- In ion traps, the trajectories of the particles are influenced by a high-frequency field.
- Quadrupole mass spectrometers (QMS) exploit the resonance of moving ions in a high-frequency field (similar to ion traps).
How does a mass spectrometer work?
- Through the inlet system, the gases to be analyzed are admitted into the chamber, for example via capillaries or a metering valve, and pumped down to the operating pressure using the vacuum system.
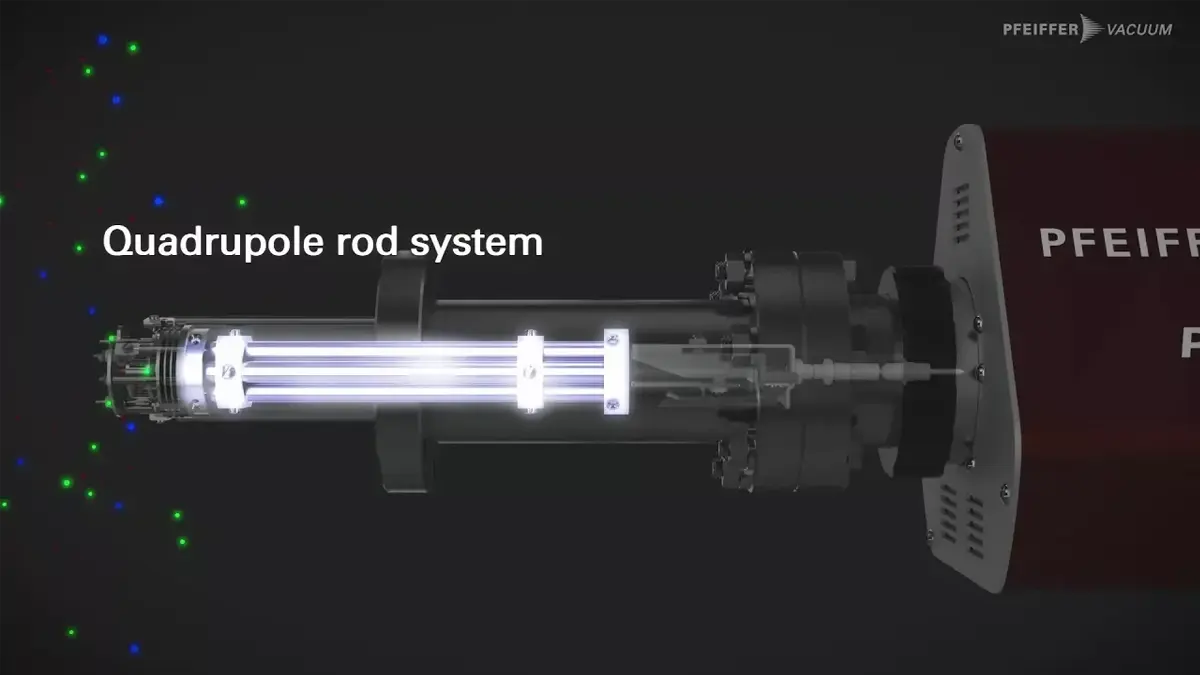
- Previously neutral gas molecules are ionized by bombarding them with electrons via the ion source and separated in the mass filter (quadrupole rod system) according to the mass to charge ratio (m/z).
- Behind the separator system, a detector measures the ion current. The ion current is a measure of the partial pressure of the respective gas component or of fragments of the same mass generated in the ion source.
- The ion source, mass filter and detector together form the actual analyzer.
- Only one mass range is always considered per time interval, meaning different masses are analyzed sequentially, not simultaneously.
How does the QMS staff system work?
Four parallel rods arranged in a square form the filter system. Between them lies a circle with the so-called field radius r0. Two opposing rods are connected, with one pair positively charged and the other negatively charged.An electrical voltage, composed of a direct voltage and an alternating voltage component, is applied between the two pairs of rods, resulting in the quadrupole deflection voltage Uquad = U + V · cos ωt. Ions of different masses are injected axially into the rod system with approximately the same energy. The quadrupole field deflects the ions in the x and y directions, filtering them by mass. If the deflection is smaller than r0, the ions reach the detector; otherwise, they do not. This can be clearly seen in the video:
Which mass spectrometer suits my application?
Mass spectrometers, also known as RGA for short, determine partial pressures, while vacuum measuring tubes are used to measure total pressure. Only gas measurement is possible, which includes the analysis of solid or liquid substances once they have been evaporated.
Important decision criteria for device selection are:
- The pressure range and the associated design
- Analytical performance, including masses to be detected, resolution, detection limit, measurement speed
How can I set up the PrismaPro quickly?
Quick setup guide
Explore the PrismaPro mass spectrometer with our quick setup guide. This guide provides clear and concise instructions to help you get your PrismaPro up and running swiftly. With step-by-step directions, you'll learn how to connect, configure, and operate the device efficiently. The PrismaPro is designed for high sensitivity and fast measurement rates, ideal for applications such as leak detection and gas analysis. Enhance your analytical capabilities with ease using the PrismaPro quick setup guide.What is the influence of the pressure range on the construction of a vacuum system?
The gases in a chamber that has been pumped down to low pressure are prepared for analysis by ionizing the electrons. The ions generated in this way are separated in a mass filter according to their mass-to-charge ratio. High vacuum is a mandatory requirement for these processes. Accordingly, the pressure range in which the gas is to be analyzed usually also dictates the design.
Construction
For residual gas analysis in the vacuum system, no additional pumps are typically required to reduce the pressure to < 5 ∙ 10−4 hPa (mbar). Therefore, standalone components are used, which consist basically of the mass spectrometer itself.Complete systems are used when the existing gas pressure required for the analysis needs to be reduced further by pumping via a gas inlet system.
Areas of application
If low pressure and therefore molecular flow are already present, the pressure may not need to be reduced further, depending on the required accuracy. This is known as residual gas analysis in the vacuum system. For example, if the gas to be examined is at atmospheric pressure, components are required to reduce the pressure. This is called gas analysis at atmospheric pressure.Are the mass spectrometers ready-made complete solutions or individual devices?
In practice, different components are chosen to fulfill various types of measurement tasks. From ready-made complete solutions such as the OmniStar to individual devices like the compact quadrupole mass spectrometer PrismaPro, there is a suitable solution for every application.